The Fiber of Self-Discipline: How to Develop and Strengthen Your Willpower
***freeDIGIBOOK***Personal Growth and Development: The Power
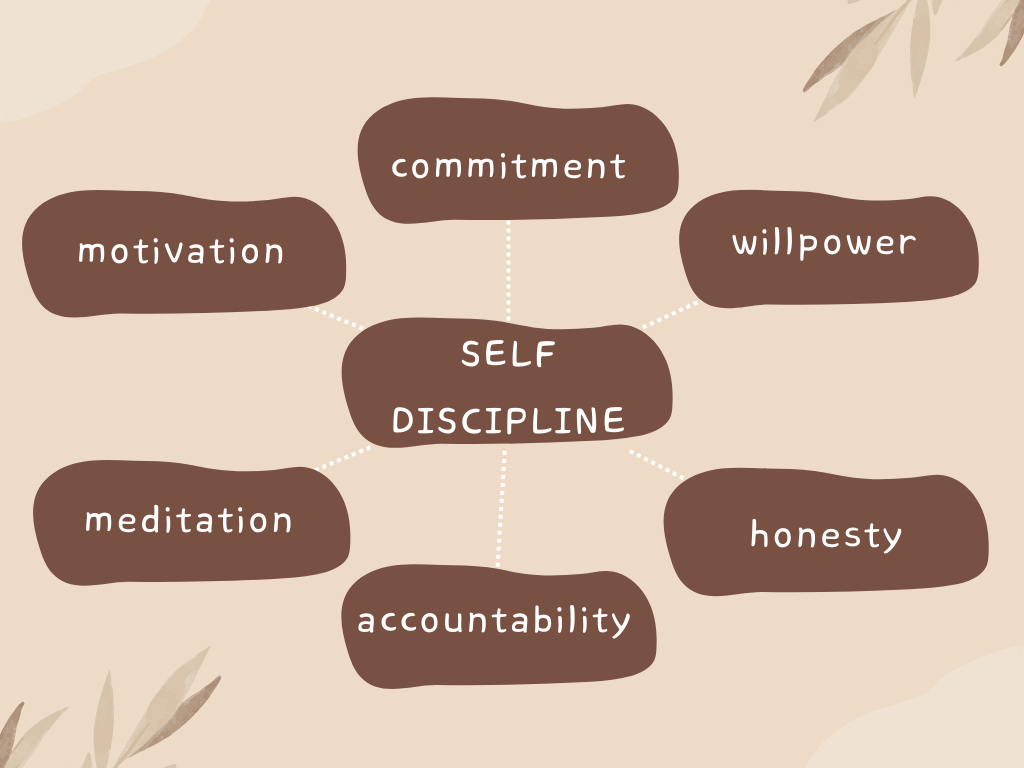
Chapter 1: Introduction to Self-Discipline
Definition of self-discipline
Importance of self-discipline in achieving goals
Common misconceptions about self-discipline
Self-discipline is the ability to control one’s impulses and actions in order to achieve a desired outcome or goal. It requires a conscious effort to make choices that align with long-term goals, even in the face of temptation or distraction.
Developing self-discipline is essential in achieving success and personal growth. Without it, goals may be abandoned, progress may be slow or non-existent, and personal potential may remain unfulfilled.
There are many misconceptions about self-discipline. Some people believe it is an innate trait that cannot be learned, while others believe it requires constant struggle and sacrifice. However, self-discipline can be learned and developed through conscious effort, practice, and commitment.
In the following chapters, we will explore various aspects of self-discipline and provide practical tips and strategies for developing and strengthening this essential trait.
Chapter 2: Understanding Willpower
Definition of willpower
The science behind willpower
How willpower affects self-discipline
Willpower is the ability to control one’s thoughts and actions in order to achieve a desired outcome. It is often used interchangeably with self-discipline, but they are not the same thing. Willpower refers specifically to the ability to resist temptation or delay gratification in pursuit of a goal.
The science behind willpower is complex and involves multiple areas of the brain. The prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making and impulse control, plays a key role in the exertion of willpower. However, studies have shown that willpower is a limited resource that can become depleted over time. This means that it can be difficult to maintain self-discipline for extended periods without taking breaks or replenishing one’s willpower.
Willpower affects self-discipline by providing the strength and motivation needed to make difficult choices and resist temptation. It is the foundation upon which self-discipline is built. Without willpower, self-discipline cannot be sustained over the long-term.
Understanding the science behind willpower can help us to better manage and conserve our willpower resources. By identifying and avoiding situations that drain our willpower, we can better maintain our self-discipline and achieve our goals. In the next chapters, we will explore practical tips and strategies for building and strengthening our willpower and self-discipline.
Chapter 3: Identifying Your Goals
Importance of setting goals
How to identify your goals
Making goals SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound)
Setting clear and specific goals is a crucial step in developing self-discipline. Without a clear direction or purpose, it can be difficult to maintain focus and motivation over the long-term.
Identifying your goals begins with reflecting on your values and aspirations. What do you want to achieve? What is important to you? What are your long-term and short-term priorities?
Once you have a general idea of your goals, it is important to make them specific and measurable. This is where the SMART framework comes in. SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Specific: Your goals should be clear and specific, with a clear outcome in mind. For example, “I want to lose 10 pounds” is more specific than “I want to be healthier.”
Measurable: Your goals should be measurable, so that you can track your progress and adjust your approach as needed. For example, “I want to save $500 per month” is measurable.
Achievable: Your goals should be challenging but achievable, based on your current abilities and resources. Setting unrealistic goals can lead to discouragement and frustration.
Relevant: Your goals should be relevant to your overall values and aspirations. Make sure that your goals align with your long-term vision for your life.
Time-bound: Your goals should have a specific timeframe or deadline, which can help to maintain motivation and focus. For example, “I want to run a 5K in 3 months” has a specific deadline.
By making your goals SMART, you can increase your chances of success and maintain your self-discipline over the long-term. In the next chapters, we will explore how to turn your goals into actionable plans and how to maintain motivation and focus.
Chapter 4: Creating Habits
Importance of habits in developing self-discipline
How habits are formed
How to create new habits and break bad ones.
Habits are powerful tools for developing self-discipline. They are automatic behaviors that we perform regularly and can be either beneficial or detrimental to our goals.
Habits are formed through a process called habituation, in which a behavior becomes increasingly automatic and less conscious over time. This process involves three stages: cue, routine, and reward. The cue triggers the behavior, the routine is the behavior itself, and the reward reinforces the behavior and reinforces its future repetition.
To create new habits, it is important to identify the cue, routine, and reward for the behavior you want to establish. For example, if you want to establish a habit of exercising every morning, your cue could be waking up, your routine could be doing a 30-minute workout, and your reward could be a healthy breakfast.
Breaking bad habits involves identifying the cue and reward for the behavior you want to change, and then replacing the routine with a more beneficial behavior. For example, if you want to break the habit of eating junk food when you feel stressed, you could identify the cue as stress, the routine as eating junk food, and the reward as feeling better. You could then replace the routine with a healthier behavior, such as going for a walk or practicing mindfulness.
To create and break habits successfully, it is important to make the behavior as easy and convenient as possible. This means removing barriers to the behavior, such as setting out your exercise clothes the night before or keeping healthy snacks readily available.
By creating beneficial habits and breaking bad ones, you can establish a foundation of self-discipline that will help you achieve your goals over the long-term. In the next chapters, we will explore how to maintain motivation and focus and how to overcome obstacles to self-discipline.
Chapter 5: Mindset and Attitude
The role of mindset and attitude in self-discipline
Developing a growth mindset
The power of positive thinking
Mindset and attitude play a crucial role in developing and maintaining self-discipline. The way we think about ourselves and our abilities can have a powerful impact on our motivation, focus, and ability to overcome obstacles.
Developing a growth mindset is one way to cultivate a positive attitude and increase self-discipline. A growth mindset is the belief that our abilities and intelligence can be developed through effort and practice, rather than being fixed traits. By adopting a growth mindset, we can approach challenges with a sense of curiosity and a willingness to learn, rather than being discouraged by failure.
Positive thinking is another powerful tool for developing self-discipline. By focusing on positive outcomes and possibilities, we can increase motivation and maintain focus. This does not mean ignoring negative thoughts or challenges, but rather reframing them in a positive light and seeking solutions.
To develop a positive mindset and attitude, it can be helpful to practice mindfulness and gratitude. Mindfulness involves being present and aware of our thoughts and emotions, while gratitude involves focusing on the positive aspects of our lives and expressing appreciation for them.
By adopting a positive mindset and attitude, we can increase our self-discipline and develop a sense of resilience in the face of challenges. In the next chapters, we will explore how to build self-discipline through strategies such as accountability and support, self-care and well-being, and maintaining momentum.
Chapter 6: Strategies for Building Self-Discipline
Tips and strategies for building self-discipline
Using visualization and affirmations
Learning to say no and setting boundaries.
Building self-discipline requires intentional effort and commitment. Here are some tips and strategies to help you develop and strengthen your self-discipline:
Set realistic goals: Make sure your goals are achievable and relevant to your overall vision for your life.
Break down your goals into smaller steps: This will make your goals more manageable and help you stay motivated.
Use visualization and affirmations: Visualize yourself achieving your goals and use positive affirmations to reinforce your motivation.
Prioritize self-care: Take care of your physical and mental health, which will help you maintain focus and motivation.
Learn to say no and set boundaries: Saying no to distractions and obligations that don’t align with your goals is an important aspect of self-discipline.
Practice self-control: Practice delaying gratification and resisting temptation in order to build your willpower and self-discipline.
Celebrate your successes: Celebrate your progress and accomplishments along the way, which will help you stay motivated and maintain momentum.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can develop and strengthen your self-discipline and achieve your goals over the long-term. In the next chapters, we will explore how to maintain motivation and focus, overcome obstacles to self-discipline, and build a support network for accountability and encouragement.
Chapter 7: Overcoming Obstacles
Common obstacles to self-discipline
Strategies for overcoming procrastination, distractions, and other obstacles.
Dealing with setbacks and failures
Even with the best intentions and strategies, obstacles to self-discipline can arise. Here are some common obstacles and strategies for overcoming them:
Procrastination: One of the most common obstacles to self-discipline is procrastination. To overcome procrastination, break down your goals into smaller steps, use visualization and affirmations to stay motivated, and hold yourself accountable for progress.
Distractions: Distractions can be a major obstacle to self-discipline. To overcome distractions, create a focused work environment, turn off notifications on your phone or computer, and use time-blocking to schedule your day.
Lack of motivation: Motivation can ebb and flow, but it’s important to stay motivated in order to maintain self-discipline. To overcome lack of motivation, revisit your goals and visualize yourself achieving them, use positive affirmations, and reward yourself for progress.
Setbacks and failures: Setbacks and failures are inevitable, but they don’t have to derail your self-discipline. To overcome setbacks and failures, reevaluate your goals and strategy, learn from your mistakes, and use setbacks as an opportunity to grow and improve.
Lack of support: Lack of support can make self-discipline more challenging. To overcome this obstacle, build a support network of friends, family, or colleagues who can provide accountability and encouragement.
By recognizing and proactively addressing obstacles to self-discipline, you can build resilience and maintain focus on achieving your goals over the long-term. In the next chapters, we will explore how to build self-discipline through self-care and well-being, accountability and support, and maintaining momentum.
Chapter 8: Self-Care and Well-Being
The importance of self-care in developing self-discipline
How to prioritize self-care and manage stress
The role of sleep and nutrition in self-discipline
Self-care and well-being are important components of self-discipline. Without taking care of ourselves, it can be difficult to maintain focus and motivation over the long-term.
Here are some tips for prioritizing self-care and managing stress:
Prioritize self-care: Make time for activities that bring you joy and relaxation, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies.
Manage stress: Stress can undermine self-discipline, so it’s important to find healthy ways to manage stress. This could include mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or talking to a friend or therapist.
Get enough sleep: Sleep is essential for cognitive function, mood, and overall health. Prioritize getting 7-9 hours of sleep per night to maintain focus and motivation.
Eat a balanced diet: Proper nutrition is important for physical and mental well-being. Aim to eat a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
Take breaks: It’s important to take breaks throughout the day to prevent burnout and maintain focus. Try taking a short walk or practicing a mindfulness exercise during breaks.
By prioritizing self-care and well-being, you can build resilience and maintain self-discipline over the long-term. In the next chapters, we will explore how to build self-discipline through accountability and support, maintaining momentum, and cultivating a growth mindset.
Chapter 9: Accountability and Support
The role of accountability and support in developing self-discipline
Finding an accountability partner
Joining a support group or community
Accountability and support are important factors in developing and maintaining self-discipline. By having someone or a community to hold you accountable and provide encouragement, you can increase your motivation and maintain focus on your goals.
Here are some tips for finding accountability and support:
Find an accountability partner: An accountability partner is someone who can help keep you on track and hold you accountable for progress. This could be a friend, family member, or colleague who shares similar goals.
Join a support group or community: Joining a support group or community can provide a sense of belonging and encouragement. This could be an online community, a local group, or a professional organization.
Use a self-tracking system: Tracking your progress towards your goals can help you stay accountable and motivated. This could be a journal, a habit-tracking app, or a calendar.
Hire a coach or mentor: A coach or mentor can provide personalized support and guidance towards achieving your goals.
By finding accountability and support, you can increase your chances of success and maintain self-discipline over the long-term. In the next chapter, we will explore how to maintain momentum and avoid burnout.
Chapter 10: Maintaining Self-Discipline
How to maintain self-discipline over the long-term
Celebrating successes and staying motivated
Continually assessing and adjusting goals and strategies
Maintaining self-discipline over the long-term requires ongoing effort and commitment.
Here are some tips for staying motivated and avoiding burnout:
Celebrate successes: Celebrate your progress and accomplishments along the way, which can help you stay motivated and maintain momentum.
Continually assess and adjust goals and strategies: As you progress towards your goals, it’s important to continually reassess and adjust your approach as needed. This could include adjusting your timeline or breaking down your goals into smaller steps.
Stay motivated: Stay motivated by visualizing your goals, using positive affirmations, and reminding yourself of the benefits of achieving your goals.
Avoid burnout: Avoid burnout by taking breaks, prioritizing self-care and well-being, and asking for help when needed.
Seek feedback: Seek feedback from an accountability partner, mentor, or coach, which can help you identify areas for improvement and stay on track.
By maintaining self-discipline over the long-term, you can achieve your goals and build a strong sense of self-efficacy and resilience. Remember to stay focused on your vision and take intentional steps towards achieving your goals, even when obstacles arise.
Epilogue: The Journey Continues
Reflections on your journey to develop self-discipline.
Encouragement to continue developing and strengthening your willpower.
Final thoughts on the importance of self-discipline in achieving success.
Congratulations on your journey to develop self-discipline! By reading this book and taking intentional steps towards building your willpower, you have already made great progress towards achieving your goals.
Remember that developing self-discipline is an ongoing journey, and there will inevitably be ups and downs along the way. Reflect on your progress and celebrate your successes, while also staying open to feedback and areas for improvement.
As you continue to develop and strengthen your willpower, remember that self-discipline is a powerful tool for achieving success and living a fulfilling life. By staying focused on your goals, prioritizing self-care and well-being, and seeking accountability and support, you can achieve great things and build a strong sense of resilience and self-efficacy.
Thank you for taking this journey with us, and we wish you all the best in your continued pursuit of self-discipline and success.



This website is mostly a walk-by means of for all the info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse right here, and also you’ll positively uncover it.
Great blog right here! Additionally your website rather a lot up very fast! What web host are you the use of? Can I get your associate link for your host? I desire my web site loaded up as fast as yours lol
Hey! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any trouble with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing months of hard work due to no back up. Do you have any methods to stop hackers?